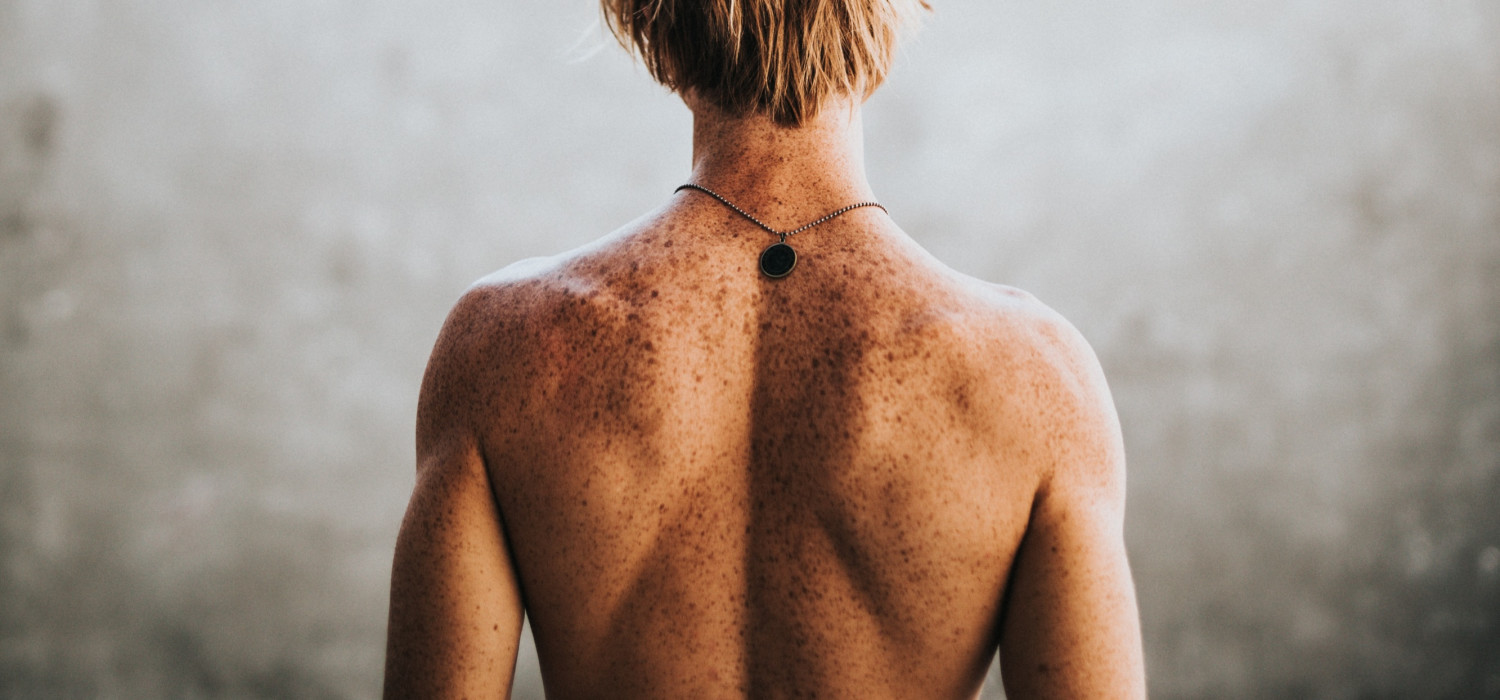
It feels like a constant weight on your shoulders. The tension in your neck and upper back never seems to go away. You sometimes get headaches from the neck tightness. Sounds familiar?
You could be suffering from tight traps and trapezius pain, which can be frustrating conditions. However, with the right exercises, you can manage and reduce the pain. This Injurymap guide gives you the information you need for treating and preventing trapezius pain. Remember to always see a medical professional if your symptoms are severe or persistent.
- What is the trapezius? What does it do?
- Causes of trapezius pain
- Exercises for trapezius pain relief
- Other treatment and relief options for trapezius pain
- When to see a doctor
- Exercise is the cure for tight traps
What is the trapezius? What does it do?
The trapezius is a flat, triangular muscle that extends from the back of the head to the neck. It is located very close to the skin. This large, strong muscle has many actions, including the movement of the neck and scapula (shoulder blade). There is a pair of trapezius muscles (commonly called the traps) present in the human body. One trap muscle is located on either side of the cervical spine (neck). Together, they form a diamond-shaped (trapezoid) muscle that covers the upper back, shoulders, and neck.1
The trapezius is important for the stabilization of the shoulder blade. It also participates in many head and neck movements. The trap muscles play an important role in posture. They support the spine and allow you to remain erect while standing.1 The trapezius muscle is divided into three parts – the upper, middle, and lower. Each part does something different.
Commmon movements where the trapezius is used
- Shrugging your shoulders
- Turning your head
- Side bending your neck
- Extending your neck backwards
- Throwing an object2,3
Modern-day inactive lifestyles are making trapezius pain more common. Nowadays, it is not unusual for someone to spend long hours at their desk in front of a computer. The seating posture keeps the trapezius continuously activated for large parts of the day. Constant use of the trapezius muscle increases the risk of developing spasm and pain. The term “tight traps” refers to spasm and pain in the trapezius muscles. Tight traps can cause significant reduction in head and neck movement.2
The traps are also prone to develop trigger points (specific spots in the muscle that become irritated and painful).2 Furthermore, whiplash injuries can also affect the trapezius.1
Pain in the trapezius muscles can be referred to other areas. This means the pain is felt in a part of the body other than the trapezius. For example, trapezius pain can lead to sinus discomfort.1 Trapezius spasms can cause tension headaches on both sides of the head, including the forehead region.3
Fortunately, the trapezius muscle responds well to exercise. There are several exercises for the trapezius that can keep it working properly without pain.
Causes of trapezius pain
The trapezius is divided into three functional parts. The upper trapezius is used to elevate the shoulder and rotate and tilt the neck. The middle trapezius moves the shoulder blade back and stabilizes it. The lower trapezius is involved in moving the shoulder blade down.4
Trapezius pain can occur for many reasons. You will often find that it is accompanied by other symptoms such as muscle stiffness, tightness, and spasms (involuntary twitches). You may also feel a numbness or tingling in the arms on one or both sides. The symptoms can result in a reduced range of motion in the neck and shoulders.
Typically, the upper part of the trapezius is involved with spasm and pain. Some of the most common causes of trapezius pain are listed below.4
1. Overuse
Repetitive activities, such as lifting heavy objects or swimming can lead to trapezius pain. People who perform monotonous work with the neck and shoulder muscles are at high risk of trapezius pain . Examples include nurses who lift and turn patients, construction workers who carry heavy objects, and retail workers who lift heavy boxes and bags.5
2. Poor posture
Sitting hunched over a desk or computer keyboard can cause your trapezius muscles to tighten. People with constrained work postures are also at risk of developing trapezius symptoms. Examples include coal miners and baggage handlers who work in confined spaces, such as the baggage compartment of commercial airplanes.
3. Mental stress
Psychological stress can lead to long lasting muscle tension in the neck and shoulders, causing symptoms like trapezius pain. Studies have shown that mental stressors can increase the activity of the trapezius muscle.6 This increase in muscle activity increases the risk of trapezius muscle pain.
4. Injury
A violent twist or collision that places excessive force on the upper back can lead to a trapezius muscle tear and pain. The muscle can get injured during contact sports, weightlifting, car collisions, and hard falls. The symptoms are usually felt immediately. The severity of the pain depends on the severity of the injury.7